Understanding Composite Fillings: A Complete Guide
Composite fillings have revolutionized dental care, offering a seamless blend of functionality and aesthetics. This comprehensive guide aims to shed light on the significance and advantages of composite fillings in restorative dentistry.
Composite fillings, also known as tooth-colored or white fillings, are a popular choice for repairing teeth affected by decay or damage. Unlike traditional silver amalgam fillings, composite fillings are made from a mixture of plastic resin and finely ground glass particles, matching the natural color of the tooth. This allows for a more natural appearance, blending seamlessly with the surrounding tooth structure.
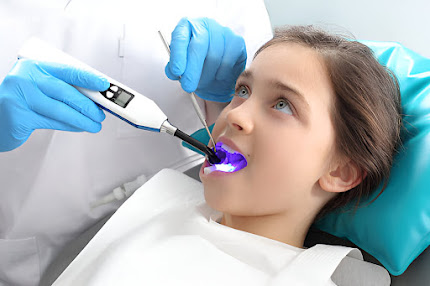
The process of placing composite fillings involves several steps. Initially, the dentist numbs the area around the affected tooth, removes the decayed portion, and thoroughly cleans the cavity. The composite material is then applied in layers, with each layer hardened using a special curing light. Once the cavity is filled, the dentist shapes and polishes the composite to ensure a comfortable bite and a natural-looking result.
One of the significant advantages of composite fillings is their versatility. They can be used not only for filling cavities but also for repairing chipped, cracked, or worn teeth. Additionally, composite fillings bond directly to the tooth, providing more support and helping to prevent fractures and further decay.
Furthermore, composite fillings are a safer option compared to traditional amalgam fillings, as they don't contain mercury, eliminating any potential concerns about mercury exposure.
Understanding composite fillings underscores their role in both restoring dental health and maintaining a natural-looking smile. Consulting with a kid's dentist near Clear Lake City can provide personalized guidance and ensure the most effective use of composite fillings for optimal dental restoration.


Comments
Post a Comment